Chemokines Brochure
Chemokines: Multifaceted Regulators of Physiology and Pathophysiology
Chemokines
The immune system is comprised of an arsenal of several cell types, each having distinct and specialized functions, that allow for quick and efficient responses to invasive foreign agents. The invasion of such matter generates an onslaught of inflammatory responses, recruiting several immune cells and proteins, including a special class of small cytokines called chemokines.
Representing the largest class of cytokines, chemokines play an essential role in both physiological and pathological activities by stimulating the migration of certain leukocytes through concentration gradients in a process known as chemotaxis.
Critical to maintaining hemostasis through hematopoietic differentiation and immune surveillance, chemokines also help orchestrate both innate and adaptive immune responses. Chemokine-triggered immune responses often require co-stimulation by primary proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-1α, IFN-γ and TNF-α. Chemokines possess high levels of specificity; a trait that enables the recruitment of diverse populations of well-defined chemokine subsets and receptors.
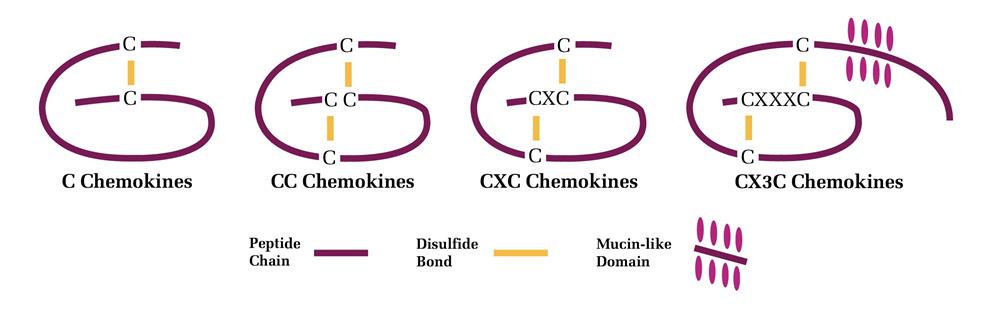
Classified into subfamilies by the structural conservation of both cysteine residues and disulfide bonds, chemokine nomenclature reflects several cysteine-grouping motifs and arrangements. Exempting members of a single subfamily, one of two conserved disulfide bonds link the first cysteine residue to the third, while the other links the second cysteine to the fourth. These disulfide bonds contribute to the tertiary and quaternary structures that further define the subfamilies and dictate possible receptor-ligand interactions.
In order to exert biological effect, chemokines will bind with receptors of the G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR) superfamily, which possess seven conserved transmembrane domains with which chemokines can interact. Classified into subfamilies based on the motifs of their ligands, these receptors tend to interact with the chemokines of their eponymous subfamilies. Chemokines and their receptors otherwise tend to interact indiscriminately to stimulate upregulation of adherent chemokines, co-stimulatory cytokines and signaling cascades that polarizes cells to direct chemotaxis.
Chemokine Subfamilies and Nomenclature
C Chemokines: Contain only two conserved cysteine residues linked by a single disulfide bond.
CC Chemokines: Contain four conserved cysteine residues of which the first two, closest to the N-terminal, are adjacent to one another.
CXC Chemokines: Contain four conserved cysteine residues of which the first two, closest to the N-terminal, are separated by a single amino acid.
CX3C Chemokines: Contain four conserved cysteine residues of which the first two, closest to the N-terminal, are separated by three amino acids.
Structure of Chemokine Classes
Examples
CXCL6, also known as GCP-2 in humans or LIX in mice, is a connective tissue-derived CXC chemokine that signals through the CXCR1 and CXCR2 receptors. Expressed in monocytes, platelets, endothelial cells and mast cells, CXCL6 is a highly selective chemoattractant of neutrophils and exhibits anti-angiogenic activity that suggests cancer-fighting potential.
| Related Research Interests: | ||
| • Angiogenesis/Cardiovascular | • Bone, Skeletal, Cartilage | • Chemotaxis |
| • Immune System | • Inflammation | • Wound Healing |
Eotaxin (CCL11) is a CC chemokine produced by IFN-γ-stimulated endothelial cells and TNF-activated monocytes that signals through the CCR3 receptor. Eotaxin selectively chemoattracts eosinophils and, along with eotaxin-2 and eotaxin-3, plays a key role in the regulation of eosinophil recruitment in asthmatic lung and allergic reactions.
| Related Research Interests: | ||
| • Chemotaxis | • Immune System | • Neurobiology |
| • Wound Healing | ||
CXCL1, also known as GRO-α/MGSA in humans, KC in mice and CINC-1 in rats, is a CXC chemokine secreted predominately by splenic cells that contributes to neutrophil activation during inflammation. CXCL1 also contributes to melanoma-related pathogenesis through stimulation of mitogenesis.
| Related Research Interests: | ||
| • Angiogenesis/Cardiovascular | • Chemotaxis | • Immune System |
| • Inflammation | • Neurobiology | • Wound Healing |
RANTES (CCL5) is a CC chemokine that can signal through the CCR1, CCR3, CCR5 and US28 (cytomegalovirus) receptors. A chemoattractant of monocytes, memory T cells (CD4+/CD45RO), basophils and eosinophils, RANTES also has the capability to inhibit certain strains of HIV-1, HIV-2 and SIV.
| Related Research Interests: | ||
| • AIDS/HIV | • Allergy | • Angiogenesis/Cardiovascular |
| • Chemotaxis | • Immune System | • Inflammation |
| • Neurobiology | • Transplantation | • Wound Healing |
Exodus-2 (CCL21) is CC chemokine expressed in lymphatic endothelial cells, the spleen and appendix. Through interaction with the CCR7 receptor, Exodus−2 chemoattracts both T and B lymphocytes to inhibit hematopoiesis.
| Related Research Interests: | ||
| • AIDS/HIV | • Chemotaxis | • Immune System |
| • Inflammation | • Wound Healing | |
TARC (CCL17) is a CC chemokine predominantly produced by thymic dendritic cells that signal through the CCR4 receptor expressed on natural killer cells, basophils and type 2 helper T lymphocytes.
| Related Research Interests: | ||
| • Chemotaxis | • Immune System | • Wound Healing |
|
CXC Systematic Name |
PeproTech Recombinant Chemokines |
RUO Chemokines |
Antibody Products |
ELISA Development Kits |
|
|
|
Catalog Numbers |
||
|
C Chemokines |
||||
|
XCL1 |
Human Lymphotactin (XCL1) |
|
||
|
CC Chemokines |
||||
|
CCL1 |
Human I-309 (CCL1) |
|
||
|
CCL2 |
Human MCP-1 (CCL2) |
|||
|
Murine JE/MCP-1 (CCL2) |
||||
|
Rat MCP-1 (CCL2) |
||||
|
CCL3 |
Human MIP-1α (CCL3) |
500-P38 | 500-P38BT | 500-P38G | 500-P38GBT | 500-M74 |
||
|
Murine MIP-1α (CCL3) |
||||
|
Rat MIP-1α (CCL3) |
||||
|
CCL3L1 |
Human LD78β (CCL3L1) |
|
||
|
CCL4 |
Human MIP-1β (CCL4) |
|||
|
Murine MIP-1β (CCL4) |
||||
|
Rat MIP-1β (CCL4) |
|
|
||
|
CCL4L1 |
Human LAG-1 (CCL4L1) |
|
|
|
|
CCL5 |
Human RANTES (CCL5) |
|||
|
Murine RANTES (CCL5) |
||||
|
Rat RANTES (CCL5) |
||||
|
CCL6 |
Murine C10 (CCL6) |
|
||
|
CCL7 |
Human MCP-3 (CCL7) |
|
||
|
Murine MCP-3 (CCL7) |
||||
|
CCL8 |
Human MCP-2 (CCL8) |
|||
|
Murine MCP-2 (CCL8) |
|
|||
|
CCL9/10 |
Murine MIP-1γ (CCL9/10) |
|
||
|
CCL11 |
Human Eotaxin (CCL11) |
500-P41 | 500-P41BT | 500-P41G | 500-P41GBT | 500-M25 |
||
|
Murine Eotaxin (CCL11) |
||||
|
CCL12 |
Murine MCP-5 (CCL12) |
|
||
|
CCL13 |
Human MCP-4 (CCL13) |
500-P04 | 500-P04BT | 500-P04G | 500-P04GBT | 500-M70 |
|
|
|
CCL14 |
Human HCC-1 (CCL14) (72 a.a.) |
|
||
|
Human HCC-1 (CCL14) (66 a.a.) |
|
|
||
|
CCL15 |
Human MIP-5 (CCL15) |
|
||
|
CCL16 |
Human LEC (CCL16) |
|
||
|
CCL17 |
Human TARC (CCL17) |
|
||
|
Murine TARC (CCL17) |
|
|
||
|
CCL18 |
Human MIP-4 (CCL18) |
|
||
|
CCL19 |
Human MIP-3β (CCL19) |
|
||
|
Murine MIP-3β (CCL19) |
|
|
||
|
CCL20 |
Human MIP-3α (CCL20) |
|
||
|
Murine MIP-3α (CCL20) |
|
|
||
|
CCL21 |
Human Exodus-2 (CCL21) |
|
||
|
Murine Exodus-2 (CCL21) |
||||
|
CCL22 |
Human MDC (CCL22) (67 a.a.) |
|
||
|
Human MDC (CCL22) (69 a.a.) |
|
|
||
|
Murine MDC (CCL22) |
||||
|
CCL23 |
Human MIP-3 (CCL23) |
|
||
|
CCL24 |
Human Eotaxin-2 (CCL24) |
|
||
|
Murine Eotaxin-2 (CCL24) |
|
|||
|
CCL25 |
Human TECK (CCL25) |
|
||
|
CCL26 |
Human Eotaxin-3 (CCL26) |
|||
|
CCL27 |
Human CTACK (CCL27) |
|||
|
Murine CTACK (CCL27) |
|
|
||
|
CCL28 |
Human MEC (CCL28) |
|
||
|
Murine MEC (CCL28) |
|
|
||
|
CXC Chemokines |
||||
|
CXCL1 |
Human GRO-α/MGSA (CXCL1) |
|||
|
Murine KC (CXCL1) |
||||
|
Rat GRO/KC (CXCL1) |
||||
|
CXCL2 |
Human GRO-β (CXCL2) |
|||
|
Murine MIP-2 (CXCL2) |
||||
|
Rat GRO-β/MIP-2 (CXCL2) |
|
|||
|
CXCL3 |
Human GRO-γ (CXCL3) |
|
||
|
CXCL4 |
Human PF-4 (CXCL4) |
|
||
|
Murine PF-4 (CXCL4) |
|
|
||
|
CXCL5 |
Human ENA-78 (CXCL5) (5-78 a.a.) |
|
||
|
Human ENA-78 (CXCL5) (8-78 a.a.) |
|
|
||
|
CXCL6 |
Human GCP-2 (CXCL6) |
|
||
|
Murine LIX (CXCL6) (92 a.a.) |
|
|||
|
Murine LIX (CXCL6) (70 a.a.) |
|
|
||
|
CXCL7 |
Human NAP-2 (CXCL7) |
500-P03 | 500-P03BT | 500-P03G | 500-P03GBT | 500-M33 |
||
|
CXCL8 |
Human IL-8 (CXCL8) (77 a.a.) |
|
|
|
|
Human IL-8 (CXCL8) (72 a.a.) |
||||
|
CXCL9 |
Human MIG (CXCL9) |
|||
|
Murine MIG (CXCL9) |
|
|
||
|
CXCL10 |
Human IP-10 (CXCL10) |
|||
|
Murine IP-10 (CXCL10) |
||||
|
Rat IP-10 (CXCL10) |
||||
|
CXCL11 |
Human I-TAC (CXCL11) |
|||
|
Murine I-TAC (CXCL11) |
|
|
||
|
CXCL12 |
Human SDF-1α (CXCL12) |
|||
|
Murine SDF-1α (CXCL12) |
|
|||
|
Rat SDF-1α (CXCL12) |
|
|||
|
Human SDF-1β (CXCL12) |
|
|||
|
Murine SDF-1β (CXCL12) |
|
|
||
|
Rat SDF-1β (CXCL12) |
|
|
||
|
CXCL13 |
Human BCA-1 (CXCL13) |
|
||
|
Murine BCA-1/BLC (CXCL13) |
|
|
||
|
CXCL14 |
Human BRAK (CXCL14) |
|
||
|
CXCL15 |
Murine Lungkine (CXCL15) |
|
|
|
|
CXCL16 |
Human CXCL16 |
|||
|
Murine CXCL16 |
|
|||
|
CX3C Chemokines |
||||
|
CX3CL1 |
Human Fractalkine (CX3CL1) |
|
||
|
Rat Fractalkine (CX3CL1) |
|
|
||
Chemokine Nomenclature
|
Systematic Name |
Functional Name(s) |
Responding Cell Type(s) |
Known |
|
|
C Chemokines |
||||
|
Lymphotactin, ATAC, SCM-1 |
Tr |
XCR1 |
||
|
XCL2 |
SCM-1β |
Tr |
XCR1 |
|
|
CC Chemokines |
||||
|
I-309 (TCA-3) |
iDC, actT [Th2], Mo (PMN) |
CCR8 |
||
|
Bs, Mo, actT, NK, iDC |
CCR2, CCR4 |
|||
|
Eo, Mo, actT, NK, iDC (PMN) |
CCR1, CCR4, CCR5 |
|||
|
Mo, actT, B |
CCR1, CCR3, CCR5 |
|||
|
Mo, actT [Th1], NK, iDC |
CCR5 |
|||
|
LAG-1 gene duplication |
Mo |
CCR1, CCR5 |
||
|
Eo, Bs, Mo, actT, NK, iDC, Tm |
CCR1, CCR3, CCR4, CCR5 |
|||
|
Mo |
CCR1 |
|||
|
MCP-3 (FIC) |
Eo, Bs, Mo, actT, NK, iDC |
CCR1, CCR2, CCR3 |
||
|
Eo, Bs, Mo, actT, NK, iDC |
CCR1, CCR2B, CCR3, CCR5 |
|||
|
(MIP-1γ, MRP-2) |
(PMN, actT) |
CCR1 |
||
|
Eo, Bs, actT [Th2], iDC |
CCR3 |
|||
|
(MCP-5) |
Eo, Bs, Mo, actT, NK, iDC |
CCR2 |
||
|
MCP-4, CKβ-10 |
Eo, Bs, Mo, actT, NK, iDC |
CCR1, CCR2, CCR3 |
||
|
Eo, Mo, T |
CCR1, CCR3, CCR5 |
|||
|
MIP-5, MIP-1d, HCC-2, LKN-1 |
Mo, T |
CCR1, CCR3 |
||
|
LEC, HCC-4 |
Mo, actT [Th1] |
CCR1 |
||
|
TARC (ABCD-2) |
actT [Th2] |
CCR4 |
||
|
MIP-4, DC-CK1, PARC, AMAC-1 |
Tr, iDC |
unknown |
||
|
MIP-3β, ELC, Exodus-3, CKβ-11 |
Tr, actT, mDC |
CCR7 |
||
|
MIP-3α, LARC, Exodus-1 |
Tm, B, iDC, PMN |
CCR6 |
||
|
Exodus-2, 6Ckine, SLC |
Tr, actT, mDC |
CCR7 |
||
|
MDC, STCP-1 (ABCD-1) |
Mo, actT [Th2], NK, iDC |
CCR4 |
||
|
MIP-3, MPIF-1, CKβ-8 |
PMN, Mo, Tr |
CCR1 |
||
|
Eotaxin-2, MPIF-2, CKβ-6 |
Eo, Bs, actT [Th2], iDc, PMN, Tr |
CCR3 |
||
|
Thymocytes, Tr, iDC |
CCR9 |
|||
|
MIP-4α, Eotaxin-3 |
Eo, Bs, actT [Th2], iDC |
CCR3 |
||
|
CTACK, ILC, Eskine |
actT |
CCR10 |
||
|
actT, Tr, Eo |
CCR3, CCR10 |
|||
|
CXC Chemokines |
||||
|
PMN |
CXCR1, CXCR2 |
|||
|
PMN |
CXCR1, CXCR2 |
|||
|
PMN |
CXCR2 |
|||
|
PF-4, Oncostatin-A |
PMN, Mo |
CXCR3B |
||
|
PMN |
CXCR2 |
|||
|
PMN |
CXCR1, CXCR2 |
|||
|
NAP-2, PBP, LDGF, MDGF |
PMN |
CXCR1, CXCR2 |
||
|
IL-8, GCP-1, NAP-1 |
PMN, Bs |
CXCR1, CXCR2 |
||
|
actT [Th1], NK |
CXCR3 |
|||
|
IP-10 (CRG-2) |
Mo, actT [Th1], NK |
CXCR3 |
||
|
I-TAC, IP-9 |
actT [Th1], NK |
CXCR3, CXCR7 |
||
|
All cell types |
CXCR4, CXCR7 |
|||
|
B, (Mo) |
CXCR5 |
|||
|
BRAK, MIP-2G |
PMN, mDC (B, Mo) |
unknown |
||
|
(Lungkine) |
PMN |
unknown |
||
|
SR-PSOX |
actT |
CXCR6 |
||
|
CXCL17 |
VEGF co-regulated chemokine 1, DMC |
Mo, iDC |
unknown |
|
|
CX3C Chemokines |
||||
|
Fractalkine, Neurotactin, CX3C |
Mo, actT, NK |
CX3CR1 |
||
|
KEY |
||||
|
Tm = memory T cells |
Bs = Basophil |
Eo = Eosinophil |
PMN = neutrophils |
|
|
B = B-cells |
Tr = resting T cell |
NK = Natural Killer cells |
mDC = mature dendritic cells |
|
|
actT = activated T cell |
T = T cells |
Mo = monocyte |
iDC = immature dendritic cells |
|
